临床医学检验技术师全题库

- 文件大小:0KB
- 界面语言:简体中文
- 文件类型:Android
- 授权方式:5G系统之家
- 软件类型:装机软件
- 发布时间:2024-11-15
- 运行环境:5G系统之家
- 下载次数:494
- 软件等级:
- 安全检测: 360安全卫士 360杀毒 电脑管家
系统简介
Introduction to Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in the digital world, disrupting traditional industries and reshaping the way we perceive data security and transaction integrity. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network.
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain

Blockchain operates on the principle of a distributed database, where each participant in the network has a copy of the entire ledger. This decentralized nature ensures that no single entity has control over the data, making it highly secure against hacking and fraud. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, and once a block is added, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity of the data.
How Blockchain Works
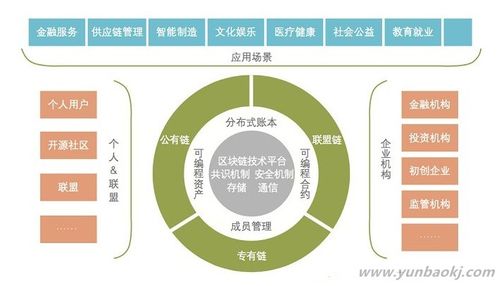
The process of adding a new block to the blockchain is known as mining. Miners use their computing power to solve complex mathematical problems, and the first to solve the problem gets to add the new block to the chain. This process is called Proof of Work (PoW), and it is what secures the blockchain. Once a block is added, it is linked to the previous block, creating a chain of blocks, hence the name \
下载地址



常见问题
- 2024-11-15 上海人社app官方版下载
- 2024-11-15 水果忍者经典版免费购买
- 2024-11-15 mindows工具箱
- 2024-11-15 比特彗星
装机软件下载排行